IP & ARP spoofing
Disclaimer: This is for educational use only.
Introduction
In the post ARP Spofing i was spoke about the ARP spoofing and how use it to get the network packages sended to another PC. In this post now, i will speak about the same thing, but with the IP, in others words, how to change the source IP of a package.
IP Spoofing
Into the IP layer of network, as is explained into this image
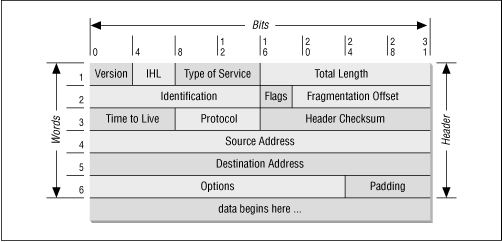
Here, will can see the Source Address field, so when a network packet (by default ;)) leave our computer, the operating system set the ip address of the output interface into that field, that is because the remote computer need response to us.
So, for example, we use cntlm proxy program with the gateway option filter by IP, the configuration
1
2
3
4
5
Gateway yes
Allow 127.0.0.1
Allow 192.168.12.3
Deny 0/0
In this example, there are 2 ips allowed to enter 127.0.0.1 for local purpose and 192.168.12.3, for example for our cellphone or another PC. Now, the atacker PC has the IP 192.168.12.4 and sniffing the network (in another post i will take about this 8)) detect what IP has access to that proxy. Our pc (has cntlm) use the IP 192.168.12.1.
Now, an atacker can do this with iptables that is the standard firewall of linux and can manipulate the network packets:
1
iptables -t nat -A POSTROUTING -p tcp --destination-port 3128 -d 192.168.12.1 -j SNAT --to-source 192.168.12.3
Explaining:
-t natUse the table nat of iptables, this is the table of routing.-A POSTROUTINGApply this rule to that packets that’s are already routed.-p tcpUse TCP protocol.--destination-port 3128The port of the proxy.-d 192.168.12.1Apply this rule to the packets that’s go to that ip192.168.12.1, if not, all the packets that will exit from our pc will change the source IP.-j SNATThis is the acction to apply, in this case, change the source of the packet.--to-source 192.168.12.3No comments :).
Ok, with this line all the packets change their source IP, but… when the remote PC respond to that request, the packet is send to that spoofed IP 192.168.12.3, so how catch the packet? Here is when is needed read the post ARP Spofing to known how tell to the PC objetive 192.168.12.1 that send the packets to 192.168.12.3 to our PC, in a short example (arpspoof we can found into the distribution repository, i use Debian -testing-):
1
arpspoof -i eth0 -t 192.168.12.1 192.168.12.3
Explaining:
-i eth0This is the network interface (can be wlan0, mon0, eth1, etc).-t 192.168.12.1This is the tarjet machine, the PC that will be apply the arp spoofing.192.168.12.13This is the address that will be spoofed.
Well and that’s all, with this all the communication is around the attacker PC and the attacked PC, even when the real IP 192.168.12.3 exists or not.